Pneumatic Tourniquet
" Handsurgery without torniquet is like reparing the watch in a barrel full of black ink "
Majority of the surgeries of the upper limb is performed in the world with the so called Ischemia.
A tourniquet can be defined as a constricting or compressing device used to control arterial and venous blood flow to a portion of an extremity for a period of time. Pressure is applied circumferentially around a portion of a limb at a desired location; this pressure is transferred to the walls of blood vessels, causing them to become temporarily occluded or restricted. In surgical settings, a tourniquet is used to occlude arterial blood flow following exsanguination to produce a relatively bloodless operative field and to minimize blood loss. Most surgical tourniquets used in surgery today are microcomputer-based, pneumatic tourniquet systems. These modern, pneumatic tourniquet systems allow more accurate and automatic pressure control, contain important safety features not possible in non-pneumatic tourniquets, and apply lower pressures and pressure gradients to the patient resulting in lower risk of patient injury.
Recent advances in tourniquet technology have led to the development of personalized tourniquet systems. These state-of-the-art modern pneumatic tourniquetsystems automatically measure the minimum pressure required to occlude or stop arterial blood flow in a limb (LOP) and recommend a cuff pressure to be used during surgery that is personalized for each individual patient based on the LOP.


They also have specially designed personalized tourniquet cuffs and matching limb protection sleeves that can conform to the limb shape and size of each individual patient. The personalization of the tourniquet instrument, cuff and sleeve for each patient further improves safety by allowing lower cuff pressures and lower pressure gradients to be used
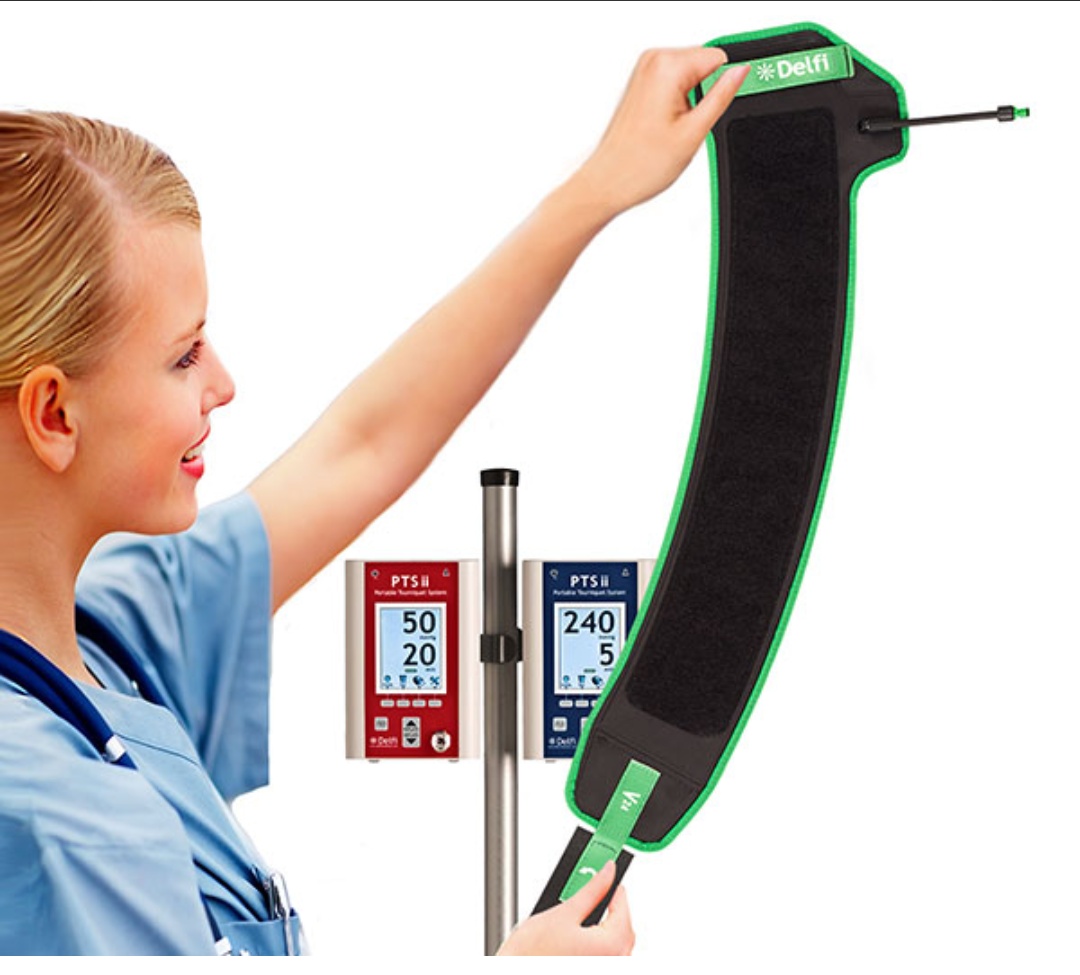

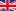
The pneumatic tourniquet can be placed around the proximal end of the arm or around the proximal end of the forearm, depending the surgery, as decided by the surgeon and anaesthesiologist. For surgeries on the finger, a tourniquet may be placed around the finger.
Once a pneumatic tourniquet has been applied, the limb is typically exsanguinated through gravity before being inflated to an occlusion pressure. As discussed earlier, high pressures and high pressure gradients result in greater risk of patient injury. Thus, a personalized, wide tourniquet cuff, and an occlusion pressure based on the patient’s LOP are recommended.
Brochure about PTS ii New Generation here
For more information, please visit https://tourniquets.org/
All material are given by permission of Prof. James A. (Jim) McEwen and http://www.delfimedical.com